How Toluene is Produced: From Crude Oil to Industrial Solvent
Understanding how toluene is produced: from crude oil to toluene industrial solvent is fundamental for appreciating its pervasive role in modern industry. This journey from raw fossil fuels to a ubiquitous chemical feedstock involves complex refining and petrochemical processes that lay the groundwork for countless manufacturing applications.
Executive Summary
- Crude oil is the primary source, undergoing fractional distillation to yield naphtha, a crucial intermediate for toluene production.
- The toluene production process is dominated by catalytic reforming, a complex petrochemical synthesis that converts low-octane naphtha into high-value aromatics like toluene.
- Industrial toluene is available in various grades, dictating its purity and suitability for specific applications, with stringent quality control measures in place.
- Safe handling, appropriate packaging, and adherence to international documentation and logistics standards are vital for the efficient and compliant trade of toluene.
Understanding Toluene: Properties and Applications
Toluene (C7H8), also known scientifically as methylbenzene, is an aromatic hydrocarbon. It appears as a colorless, water-insoluble liquid with a characteristic sweet, pungent odor reminiscent of paint thinner. Its chemical structure, featuring a benzene ring with a methyl group attached, grants it valuable solvent properties and makes it a versatile building block in chemical synthesis.
The Crude Oil to Toluene process begins with atmospheric distillation in modern refineries.
The versatility of toluene stems from its ability to dissolve a wide range of organic materials. This makes it indispensable as a solvent in the production of paints, lacquers, varnishes, adhesives, inks, and coatings. Beyond its solvent applications, toluene is a critical intermediate in the synthesis of other important chemicals such as benzene, xylene, polyurethane, and nylon, underscoring its significance in the broader chemical industry. Understanding toluene production process is thus key to grasping its market dynamics.
The Foundation: Crude Oil and Its Refining
The ultimate origin of most industrial toluene lies deep within the earth, in the form of crude oil. Crude oil is a complex mixture of thousands of hydrocarbons, along with varying amounts of sulfur, nitrogen, and oxygen compounds. To extract valuable components like toluene, crude oil must undergo a series of intricate refining processes.
The initial step in refining is fractional distillation. Crude oil is heated and introduced into a distillation column, where different hydrocarbon components separate based on their boiling points. Lighter fractions, with lower boiling points, rise to the top of the column, while heavier fractions, with higher boiling points, remain at the bottom. Among the key fractions obtained is naphtha, a volatile liquid hydrocarbon mixture that serves as the primary feedstock for petrochemical toluene synthesis.

Key Production Pathways: From Naphtha to Toluene
The transformation of naphtha into toluene involves sophisticated toluene production process pathways, primarily within the petrochemical industry. These processes are designed to maximize the yield of desired aromatic hydrocarbons.
Catalytic Reforming: The Heart of Petrochemical Toluene Synthesis
Catalytic reforming is unequivocally the most significant method for toluene production process. This process takes straight-run naphtha, typically with a low octane rating unsuitable for gasoline, and subjects it to high temperatures (around 500°C) and moderate pressures in the presence of a platinum-based catalyst. The catalyst facilitates a series of complex chemical reactions, including cyclization, dehydrogenation, and isomerization.The Crude Oil to Toluene process begins with atmospheric distillation in modern refineries.
These reactions rearrange the hydrocarbon molecules in naphtha, converting paraffins and naphthenes into a mixture rich in aromatic hydrocarbons, notably toluene, benzene, and xylenes. This resulting mixture is known as reformate. The reformate is then sent to a separation unit, often a superfractionator, where toluene is isolated from other aromatics and non-aromatics through distillation. The efficiency of petrochemical toluene synthesis via catalytic reforming is a cornerstone of the global toluene supply.

Steam Cracking: An Alternative Route to Aromatics
While catalytic reforming is the dominant source, steam cracking also contributes to toluene availability, albeit indirectly. Steam cracking involves heating hydrocarbons (such as naphtha or ethane) to very high temperatures (around 800-900°C) in the presence of steam. This process breaks down larger hydrocarbon molecules into smaller, more valuable ones, primarily light olefins like ethylene and propylene.
A co-product of steam cracking, particularly when heavier feedstocks like naphtha are used, is pyrolysis gasoline (pygas). Pyrolysis gasoline is a highly aromatic stream that contains significant amounts of toluene, xylene, and other aromatics. Toluene can be extracted from pygas through solvent extraction followed by distillation. This route adds to the overall supply of toluene but depends on the demand for olefins.
Toluene Disproportionation and Transalkylation
Beyond direct extraction from reformate or pygas, further processing steps can enhance toluene yields. Toluene disproportionation is a process where two toluene molecules react to form one molecule of benzene and one molecule of mixed xylenes. This reaction is economically favorable when benzene is in high demand.Many suppliers highlight their Crude Oil to Toluene efficiency to demonstrate competitive production costs.
Transalkylation involves reacting toluene with heavier aromatics (like C9+ aromatics) to produce benzene and xylenes. These processes are crucial for optimizing the output of the aromatic pool within a refinery or petrochemical complex, allowing producers to fine-tune their production based on market demands for benzene, toluene, and xylenes derived from toluene from naphtha processing.
Specifications and Grades of Industrial Toluen
Industrial toluene is not a monolithic product. It is typically classified into various grades, each defined by specific purity levels and impurity profiles, crucial for different industrial applications. Understanding these specifications is vital when procuring toluene.
Comparison Table: Common Toluene Grades
| Grade Name | Purity (Assay, min. %) | Key Impurities (max. ppm) | Typical Industrial Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technical Grade | 99.0 | Benzene (500), Non-Aromatics (500) | General solvent, paint thinner, ink production |
| Industrial Chemical Grade | 99.5 | Benzene (200), Non-Aromatics (300) | Chemical intermediate for TDI, benzoic acid, pharmaceutical intermediates |
| High Purity Grade | 99.8 + | Benzene (50), Non-Aromatics (100) | Specialty chemical synthesis, reagents, electronics applications |
The purity of toluene is critical. For instance, if toluene is used as a feedstock for producing toluene diisocyanate (TDI), a key component in polyurethanes, even minor impurities can negatively impact the final product quality and process efficiency. Therefore, specific grades are mandated for such sensitive applications. Regulatory limits on impurities like benzene, known for its carcinogenicity, are also strictly enforced.
Packaging and Palletization for Safe Handling
The safe and efficient transportation of toluene, a flammable liquid, requires careful consideration of packaging and palletization. The choice of packaging depends on the quantity ordered and the mode of transport.Many suppliers highlight their Crude Oil to Toluene efficiency to demonstrate competitive production costs.
Smaller quantities, often for laboratory or specialized industrial use, are typically supplied in steel drums (e.g., 200-liter drums). For bulk quantities, toluene is transported in ISO tanks, flexitanks, or via dedicated chemical tankers. Packaging must comply with international regulations for the transport of hazardous materials, including appropriate labeling and certification to ensure containment and prevent leaks.
Proper palletization is essential for drums to facilitate handling with forklifts and to secure them during transit. This minimizes the risk of damage and spillage, ensuring that the product arrives at its destination in optimal condition, ready for use in its intended industrial roles from crude oil to toluene transformative processes.

Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ) and Lead Times
The supply chain for toluene, from its origin through toluene from naphtha processing, involves significant logistical coordination. Consequently, suppliers often have Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) to ensure economic viability for production and distribution runs.
MOQs can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on the packaging type. For drummed toluene, MOQs might range from a few drums to a full pallet. For bulk shipments (ISO tanks or vessels), MOQs are considerably higher, often amounting to hundreds or thousands of metric tons.Many suppliers highlight their Crude Oil to Toluene efficiency to demonstrate competitive production costs.
Lead times, the period between placing an order and receiving the shipment, are also influenced by production schedules, raw material availability, and logistical complexities. While standard grades might have lead times of 1-4 weeks, specialized grades or large bulk orders could require longer lead times, potentially up to 6-8 weeks. It is advisable to inquire about current MOQs and lead times directly with your supplier for accurate planning of your petrochemical toluene synthesis related needs.Many suppliers highlight their Crude Oil to Toluene efficiency to demonstrate competitive production costs.
Documentation and Compliance: Essential for Traders
Trading industrial chemicals like toluene necessitates a comprehensive set of documents to ensure compliance with international trade regulations, safety standards, and quality assurances. This documentation is critical for both buyers and sellers.In the Crude Oil to Toluene pathway, catalytic reforming plays the most critical role in aromatic formation.
Mini-Checklist: Essential Toluene Trade Documents
- Certificate of Analysis (CoA): Verifies that the delivered toluene meets the specified chemical composition and purity standards.
- Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS)/Safety Data Sheet (SDS): Provides essential information on the chemical’s properties, hazards, safe handling, storage, and emergency procedures.
- Bill of Lading (B/L): A contract of carriage issued by the carrier, serving as a receipt of the goods and a document of title.
- Commercial Invoice: Details the transaction, including product description, quantity, price, and payment terms.
- Packing List: Itemizes the contents of each package or shipment.
- Certificate of Origin: Certifies the country where the toluene was manufactured.
Adherence to these documentation requirements is not merely procedural; it is a fundamental aspect of responsible chemical trading and ensures the integrity of the toluene production process and its onward journey.Many suppliers highlight their Crude Oil to Toluene efficiency to demonstrate competitive production costs.
[IMAGE INSERT 2 DESCRIPTION]
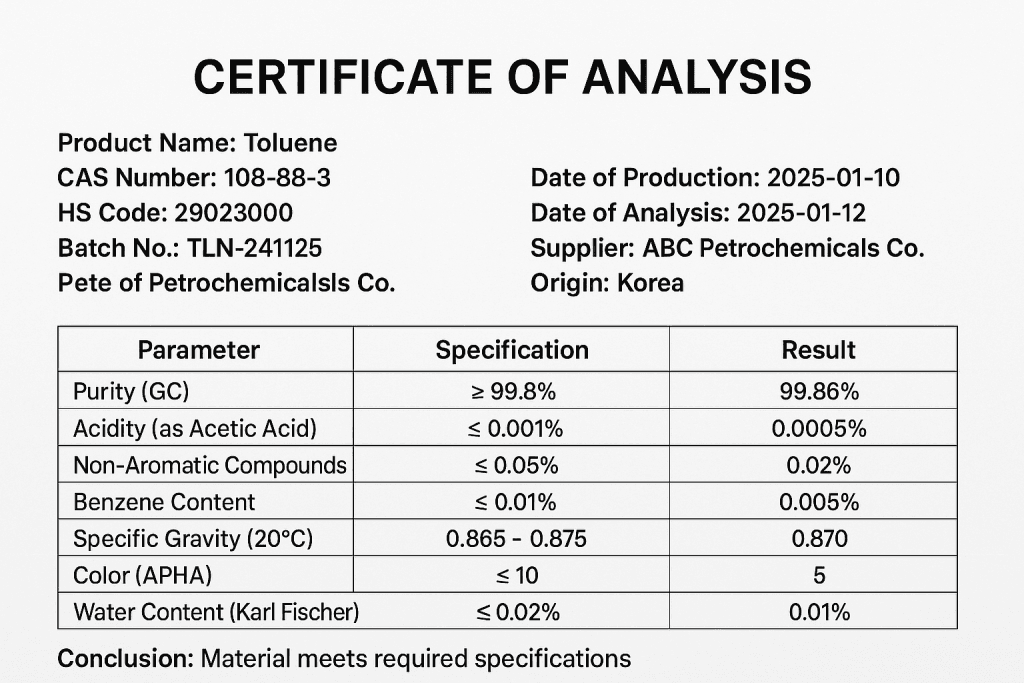
Logistics and Incoterms: Navigating Global Supply Chains
The global movement of toluene involves complex logistics governed by international commercial terms known as Incoterms. These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding costs, risks, and transportation.Understanding the Crude Oil to Toluene conversion helps buyers evaluate product purity and production reliability.
Common Incoterms for toluene include:
- FOB (Free On Board): The seller delivers the goods on board the vessel nominated by the buyer. Risk and cost transfer to the buyer once the goods are on board.
- CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight): The seller pays for the cost of the goods, insurance, and freight to the destination port. Risk transfers to the buyer upon loading onto the vessel.
- DDP (Delivered Duty Paid): The seller is responsible for delivering the goods to the buyer’s premises, cleared for import and including all duties and taxes. This is the most comprehensive term for the buyer.Many suppliers highlight their Crude Oil to Toluene efficiency to demonstrate competitive production costs.
Understanding the nuances of these terms is crucial for managing costs, insurance, and liability throughout the supply chain, from the initial crude oil to toluene conversion to final delivery.In the Crude Oil to Toluene pathway, catalytic reforming plays the most critical role in aromatic formation.
[VIDEO INSERT SUGGESTION]
- Video Suggestion: A short, animated explainer video illustrating the catalytic reforming process, showing naphtha being converted into aromatics and then separated into toluene, benzene, and xylenes.
- Video Filename: catalytic-reforming-process-toluene-explained.mp4
- Video Alt Text: Animated explanation of the petrochemical toluene synthesis process via catalytic reforming.
- Video Caption: Visualizing the intricate chemical transformations in producing toluene.

Risk Management and Claims in Toluene Trading
Despite stringent controls, risks are inherent in the trade of industrial chemicals. These can range from quality deviations and transportation damage to logistical delays or unforeseen market fluctuations that affect the value derived from toluene from naphtha.Understanding the Crude Oil to Toluene conversion helps buyers evaluate product purity and production reliability.
Effective risk management involves proactive measures such as thorough supplier vetting, robust quality control checks (e.g., third-party sampling and analysis), securing appropriate insurance coverage, and building in contingency plans for logistical disruptions.The Crude Oil to Toluene route produces high-purity solvent used in coatings, chemicals, and fuels.
In the event of a claim, it is imperative to act quickly and systematically. This typically involves notifying the supplier and/or carrier within specified timeframes, providing detailed evidence (e.g., photographs, laboratory reports, surveyor’s findings), and adhering to the complaint resolution procedures outlined in the sales contract or the applicable Incoterms. Prompt and accurate reporting is key to the successful resolution of any issues arising from the how toluene is produced: from crude oil to industrial solvent supply chain.
Conclusion: Securing Your Toluene Supply
The journey of toluene from its humble beginnings as crude oil to its status as an indispensable industrial solvent is a testament to sophisticated chemical engineering and global logistics. The primary method of toluene production process, catalytic reforming of naphtha, exemplifies the innovative nature of the petrochemical industry.In the Crude Oil to Toluene pathway, catalytic reforming plays the most critical role in aromatic formation.
Whether you require toluene for paints, adhesives, or as a crucial intermediate for advanced chemical manufacturing, understanding its production pathways, quality grades, handling requirements, and the intricacies of global trade is paramount. By working with reputable suppliers and paying close attention to documentation, logistics, and risk management, businesses can ensure a reliable and compliant supply of this vital commodity.
To secure your reliable supply of high-quality toluene, thoroughly investigate the production methods and quality assurances offered by your potential partners, ensuring they align with your industrial needs and regulatory requirements for how toluene is produced: from crude oil to industrial solvent.













